Top 5 Reasons Why Website Pages are not Being Indexed by Google? How to Fix it?

You have finally put your new website online and are excited about the visitors. But nobody comes – because after months your URLs still don’t appear in Google search results. In this article, you will learn more about possible reasons and learn how to fix errors. For a basic explanation of how Google Search works and how pages are crawled and indexed, read the following blog.
A crawler – what is it?
Even the most beautiful web presence has to be indexed so that online readers can discover it. The prerequisite for this is that the Googlebot crawls it: A program controlled by algorithms finds your website and lists all the links that should be crawled. The Googlebot takes the information and sorts it in an index with regard to its relevance and possible target groups.
Your page is never directly indexed
It repeats this process at regular intervals, so your website is not crawled just once. So, don’t panic if it doesn’t work right away – the Googlebot needs time with the mass of web information that has to be processed every day worldwide. Due to a limited crawl budget, it often does not search the entire website, but only selected pages. You can find a clear statement about this in the Google Search Console Forum. However, if too many of your pages are being ignored, you should find the sources of the error. Google does not crawl all pages on the web, and it does not index all of the pages it crawls.
No indexing: first quick measures
On the one hand, Google supports you in the search for clues in the Search Console in the “crawling” area. In the “Crawling Errors” report you can find out whether errors have occurred in the last 90 days. They could have prevented Googlebot from accessing certain areas of your website. The heading “URL errors” indicates missing 301 redirects and pages not found (404 errors). The “site query” on Google gives you an additional overview. To do this, first enter your domain in the following format in the Google search:
site: exampledomain.com
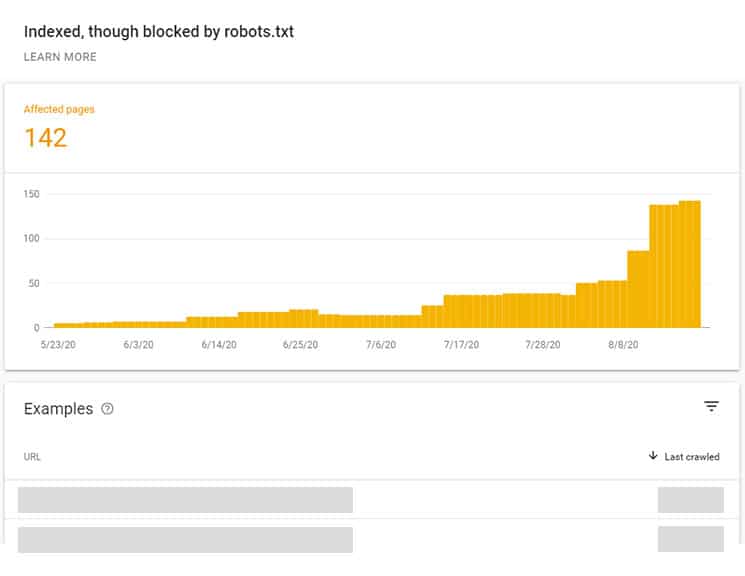
Check which pages are affected
If you are asked whether you own this domain, you should first register the page in the Google Search Console. Log in with your login and select “Add property” on the start page. Here you enter the domain. You will receive information on how to confirm your ownership. The best thing to do is to download the given code and upload it to your website. However, if your site is already “known” to Googlebot, you will see your indexed URLs at this point. Does the number of pages roughly correspond to the number posted online or are there major deviations? Check the following five points if there are any discrepancies.
1. Non-existent XML sitemap
Web crawlers like Googlebot scour the Internet for new content and wander from page to page. At least one link should lead to your page, otherwise it will remain invisible to the bot. This is not a problem with good on-page optimization – every new page will be found at some point. However, to speed up the search process, you should create an XML sitemap for Google as an indexing aid.
This is XML and this is how you work with it:
XML sitemaps are standardized text files that contain the structure of your website in machine-readable form and that search engines can easily interpret. Not only do they convey the URLs to Google, but also the date and frequency of changes, and the priority or hierarchy of the page content. Content management systems such as WordPress offer plugins and tools for creating a sitemap, but you can also create them manually. If your uncompressed sitemap is larger than 10 MB, you have to break it down into several smaller sitemaps and submit them in a sitemap index file.
Add a sitemap: Here’s how
The easiest way to submit them to Google is to use the Google Search Console’s Sitemaps tool. Log in to your account and select the relevant website. In the left tab you will find the item “Crawling” and under its “Sitemap”. If one has not yet been submitted, you will see an error message. If you click on “Add sitemap”, your URL and an empty field will appear in which you can insert the created sitemap. Google will suggest other ways for you to submit a sitemap as well. If you have a good knowledge of code changes, enter the path to your sitemap by adding the following line anywhere in your robots.txt file: sitemap: http://exampledomain.com/sitemap_location.xml
Possible sitemap errors
Even if you have already submitted the sitemap, errors can occur, which you can also identify in the “Sitemaps” area of the Search Console. Below are some of the problems that Google lists under “Sitemap errors and solutions”.
-
URLs not accessible / URL not allowed
Check that your file is in the right location and on the right level. Make sure that all URLs start with the same domain name as the location of your sitemap, i.e. uniformly with www., Http or https.
-
Unseen URLs / 404 errors
Google cannot process your sitemap completely. This happens, for example, when some URLs contain too many redirects that the Googlebot cannot retrieve. Get rid of your broken links and set up permanent redirects.
-
Invalid or incomplete URL
URLs are invalid if they contain unsupported characters, i.e. are not coded in a legible manner, or if the formatting is specified with https: // instead of http: // (or vice versa).
2. Duplicate content
Also, check to see if Google has indexed your preferred page or a different version of the domain name. If http://exampledomain.com was not indexed, add http://www.exampledomain.com and the possibly existing https version to your account. Click on your website on the Search Console homepage and enter under the gear icon “Website settings” which page Google should index.
Set the canonical tag
Also use the canonical tag to avoid duplicate content: It is placed in the header of the source code and shows the crawler which of the URLs is the original source. This can then look like this for the preferred domain:
<link rel = “canonical” href = “http://www.example.com/example.html” />
But be careful: the canonical tag is not necessary everywhere and it can cause gross crawling errors if handled incorrectly. It may not appear in the body area of the page source text or be used twice in the metadata.
3. Technical requirements for indexing
Status Codes:
Also deal with the HTTP status codes of your site: Check regularly whether 301 redirects are not working or whether 404 status codes exist. Pages with this status cannot be found for potential readers and web crawlers. Links that refer to such sites are called “dead links”.
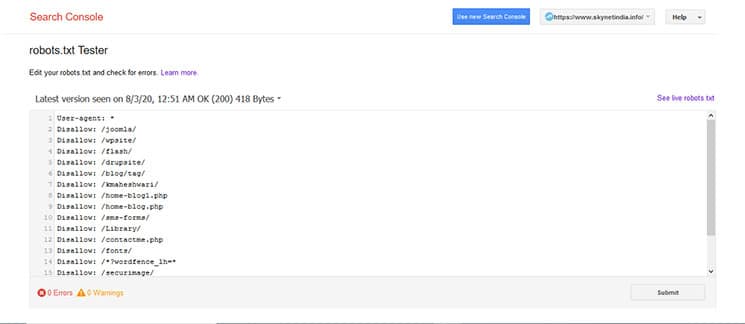
Robots.txt file:
The problem may also be in the robots.txt file. The robots.txt file is a text file that can be used to specify which areas of a domain may and may not be crawled by the search engine’s crawler. Webmasters can use it to influence the behaviour of search engine crawlers. Directories that should not be indexed can be marked with “Disallow”.
User agent: * Disallow
With this command, you tell web crawlers to ignore entire areas of the page. You can also find out whether the Googlebot is being blocked by the robots.txt with the “Access as by Google” report in the Search Console. By the way, after a relaunch at the latest, a thorough check of the robots.txt is generally recommended.
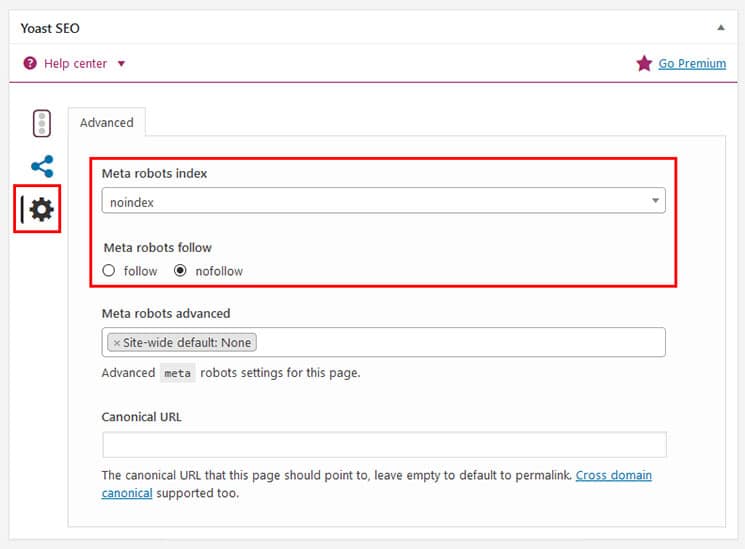
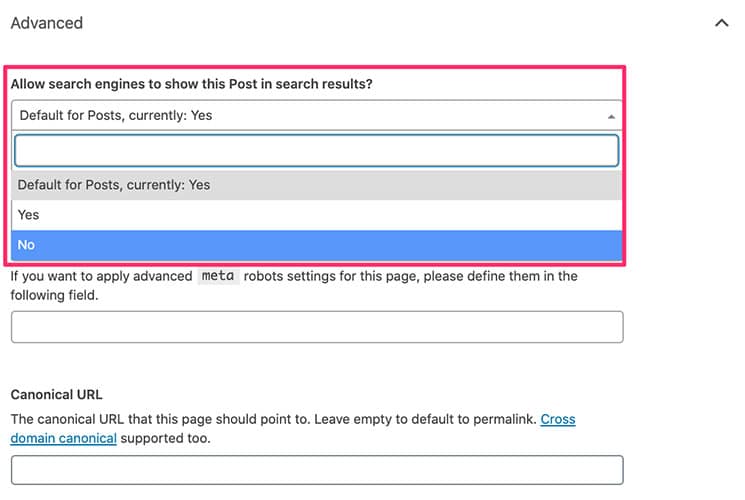
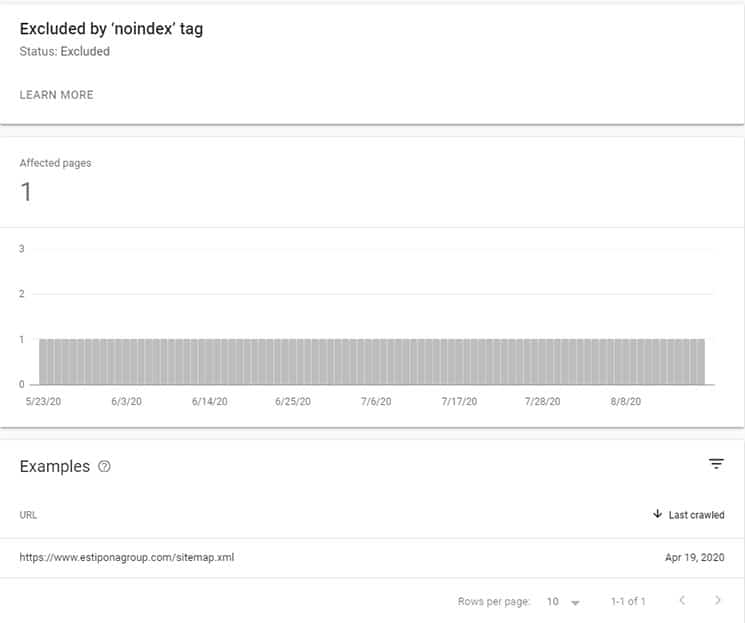
Metatag “noindex”:
With the entry “noindex” in the meta tags, a search engine robot is informed that the visited page should not be included in the index. With “noindex” webmasters have the possibility to influence the indexing of their pages. The use of the noindex tag can be useful for:
- internal search results pages
- double category pages
- copyrighted content
“Nofollow” attribute:
The rel = “nofollow” attribute is a micro-distinction in the HTML code of a website. It is used to mark-up certain links so that they are not included in the formation of the Google index. The rel = “nofollow” attribute tells the search engine robots that crawl a website that they do not have to or may not follow this link.
4. WordPress settings
If you use WordPress as a content management system and your blog is not indexed, the solution can be very close. Check in the “Settings” area in the left column whether the “the Search Engine Visibility” function is not activated. Check the option. Save Changes, and it is! WordPress will update the robots.txt file to you automatically.
5. Bad Neighborhood
When you’ve bought a domain, you’re immediately wondering which backlinks are used to get new traffic to your site. Link farms or purchased links are of course, out of the question, rather high-quality links with a thematic reference. If your page is still not indexed, look into its history. Have previous owners possibly placed bad neighborhood links, spam or hidden elements on the site?
Explain the change of ownership to Google
If a bad link points to a website or an outbound link points to a website with many bad links, then that website is in a bad neighborhood and is losing its trust from Google. It can be a bad quality link if one of the websites violates the guidelines of search engines such as Google or Bing. If the site has received a previous penalty from Google and has been deindexed for this reason, submit a ” Request to review the site ” and explain to Google that you have unknowingly taken over a domain that unfortunately did not meet Google’s guidelines. Checking and re-indexing is possible, but may take some time.
Conclusion: indexing is mandatory
The indexing of the homepage and subpages are essential for your success on the Internet. So, take the time to check for any web crawling errors with the Google Search Console. Follow the webmaster guidelines, avoid bad links and hidden text. Technical pitfalls such as incorrectly programmed robots.txt files, “nofollows” in meta tags or multiple indexing are also common reasons for poor visibility. And of course, the content has to convince Google! This rarely works with a simple landing page without links.
Do you need any help regarding why your website is not being indexed by Google? Or want to fix them? We are happy to assist you.
If you are looking for SEO Services, Social Media Services, PPC Campaign, Digital marketing Services, Please Explore our SEO Packages! We also provide regular website maintenance services from a small content update, webmaster sitemap updates, bug fixing, troubleshooting, critical security updates, SSL certification, module configuration, installation to version upgrades and much more. For more information, explore our website maintenance services.